1.Pre-filing and analytical
What is Patent?
A patent can be obtained in India either for a product or a process. Patent is a certificate which enables a company or an inventor the exclusive right to prevent third parties, who do not have his consent, from the act of making, using, offering for sale, selling, or importing for those purposes that product or process in India (section 48 of the Indian Patent Act, 1970). However, not every product or process can be patented in India. It, therefore, necessary to understand if a product or a process can be patented in India.
Patentability Analysis
Analysis of Patent is carried on the basis of following:
1.Novelty
2.Inventive step
3.Patentability
Novelty means that the invention (product or process) should be new; inventive step means that the invention should not be obvious to a skilled person and should involve or include a technical advancement and patentability means any invention that does not fall within the scope of sections 3 and 4 of the Indian Patents Act, 1970.
Global Patent Strategy
Novelty and Inventive step are the criteria’s that are followed and applicable in all the jurisdictions i.e., all over the world. It is basic requirement for any invention to obtain patent all over the world and therefore, the meaning/applicability of novelty and inventive step is same globally. Thus, if an invention (product or process) has been patented in jurisdictions such as USA, Europe, Japan, etc. it will become easier to obtain a patent in the other jurisdictions as well.
Prior Art Search
In order to establish if an invention can be patented, it is advisable to carry out a search globally, if the invention has been published or known to people anywhere in the world. A prior art search of the invention aids in analyzing the strength of the invention as well and to strategize on filing of the application for a patent.
Freedom to Operate Search
In cases where the company is aware of the existing knowledge regarding the invention but yet wants to pursue to manufacture or sell the invention, a freedom to operate search is performed. A freedom to operate search aids a company to understand the patents that are already acquired and how not to infringe/obstruct the same by his product or process. In simple words, freedom to operate enables a company to freely operate in the market where the patent is already obtained for the same or similar thing just by minor changes in his invention without it being novel or involving any inventive step.
Validity Search
After obtaining a patent, it is required to maintain the validity of the same. A validity search makes sure that the company or a person who has the rights to his invention does not get infringed by any third party. A validity search will help the company or inventor to claim damages against the infringement caused by the third party for its invention.
Patent Landscape Analysis
In case an inventor or a company comes across any new research, there is a high possibility that other people in similar field might be carrying out similar research work. Thus, a patent landscape analysis is carried out to analyze the patents obtained in similar field or research work by the competitor companies and accordingly strategize the development of the invention.
Patent drafting
What is Patent Drafting?
Patent drafting is the art of presenting a technical document in a manner to
clearly and
sufficiently express an invention in a technically detailed and legally
strong manner. It is
one of the most crucial aspects for a patent to get granted proving its
quality. To file a
patent application, it is mandatory to disclose the invention in detail so
as a skilled
person would understand the invention. A patent application disclosing all
the details
regarding the invention is known as a specification. The specification can
either be a
provisional specification or a complete specification.
Drafting of a
patent
application (specification) requires not only good technical knowledge but
legal knowledge
as well. Technical knowledge will enable a skilled person to portray its
invention in most
efficient way and legal knowledge would enable him to obtain a patent
certificate by meeting
all the requirements as per the Indian Patent Office. Patent drafting,
therefore, requires a
skilled person to understand the invention through the details as given by
the inventor and
at the same time abide by the law.
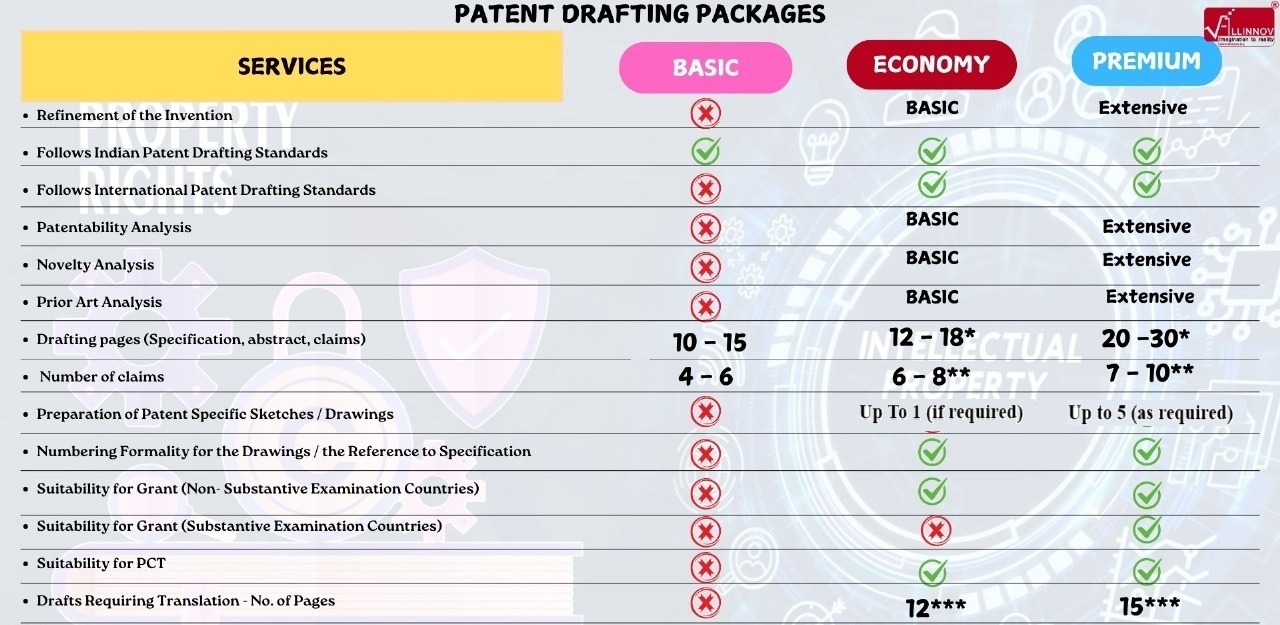
Patent Drafting Packages
* / ** / *** - Every additional page, claim and translation will be charged at INR. 500, INR. 500 and INR. 3500 respectively.
A provisional specification is a patent application which discloses details of an invention, however, the details need not be completely disclosed. Provisional specification is usually filed to claim priority of the invention i.e., to claim the earliest date of the invention to acquire a patent certificate. In India, after filing a provisional specification, one has to file a complete specification with all the details regarding the invention within twelve months from the date of the filing of the provisional specification. A provisional specification enables the inventor to opt for additional one year (twelve months) to prepare the patent application thoroughly and at the same time to claim an early priority for the invention as well. It is to be noted that, in some countries filing a provisional specification is not available.
A complete specification can either be filed directly or within one year (twelve months) from the date of filing of the provisional specification. A complete specification discloses all details of the invention such as field of the invention which it relates to, background of the invention, summary of the invention, detailed description of the invention, experimental data (examples) related to the invention, claims of the invention, abstract and drawings of the invention. A patent certificate is granted for the complete specification including all of the details as mentioned above.
Like how a fence defines the legal right of your land in a vast property or a layout, claims define the limits accurately pinpointing the scope of protection of an invention. Even though claims are a part of the specification, it is one of the most important aspects in the grant of a patent certificate. A patent is granted through analyzing claims of a complete specification. Claims play an important role for deciding the scope for which protection of the invention is acquired and on basis of which a patent certificate is granted.
Patent sketching is the art of presenting descriptive drawings in support of a patent draft (patent specification / write-up). Patent sketches usually explain the whole invention in simple pictorial form from which the specification can take reference and ensure that the person reading the draft clearly understands the invention in the right manner.
Filing
Filing Provisional / Complete specification
After all the research and development of the invention, analysis and drafting of an application, filing of the application is a crucial skill as it needs to be as per the law. Filing of provisional or complete specification requires good understanding of the law and an experienced person to guide the company or inventor as to how the law works in order to meet the requirements of the respective governments as per their jurisdictions.
Even though the governments are different in different jurisdictions, understanding the law requires a skilled person. It is necessary to abide by the law as it makes it easier for the company and the government to complete the procedural requirements and obtain a patent.
Filing of the provisional or complete specification in different jurisdiction are different but requires few essential details to be disclosed. For example, name and address of the company, name, address and nationality of the inventors, declaration by the inventors of assigning their patent rights to the company, details of their patent attorney, etc.
On filing of the application, the company or the inventor on who’s name the application is filed will become ‘Applicant’ for the said patent application.
Patent Publication (anticipated disclosure)
It is always advisable to not to disclose the details of the invention anywhere, not even in public exhibitions or conferences or in journals, as publication of the invention is very vital.
If the details regarding the invention have already been disclosed earlier, the same will become an anticipated disclosure and therefore, act as a novelty destroying criteria.
After filing of the application, the applicant is free to publish the same if it wishes to. The Patent Offices, as well, publishes the application after few months.
Filing Request for Examination / Expedited Examination
It is mandatory to file a request for examination of the application by the Applicant in order to obtain a patent. A request for examination can be filed at the time of filing of the application itself or within forty-eight months from the date of filing of the application.
The Indian Patent Office encourages filing of patent applications and grant of the same, and has therefore, introduce expedite examination as well, provided if the Applicant meets some specific requirements.
For example, if one of the Applicant is a female, or if the Applicant is financially or substantially supported by the government of India, or is a department of government of India, then a request for expedite examination can be filed.
A request for expedited examination of the application means to fast track the application and enables the Applicant to obtain a patent certificate at the earliest.
Prosecution services
‘Prosecution’ relates to the legal procedure/proceedings for obtaining a patent application between the Applicant and the Controller/Judge.
Prosecution of a patent application has two major proceedings:
- Examination Report / Office Action
- Hearing
On filing a request for examination, the Patent Office will conduct a search from its end and prepare an examination report/office action based on the technical analysis as well as based on any irregularity condoned by the Applicant for not meeting the legal requirements as per the Patent Office law.
It is mandatory to file a reply/response to the examination report or the application will be deemed to be abandoned which cannot be revived.
After filing the response/reply to the examination report, if the Controller is still not convinced, a further opportunity will be given to the Applicant through hearing. A hearing can be conducted either through video conference or in-person. In some jurisdictions, an interview through telephone can also be conducted for minor objections, if required.
Analysis of Examination Reports
As the Examination Report is prepared by the Patent Office for the Applicant which consists of objections raised by the Patent Office with respect to invention as well as the procedural shortcomings of the law, it must be appreciated that to address the said objections in the Examination Report requires a skilled person that understands the law and the technical aspect of the invention.
Thus, analyzing the Examination Report requires a qualified Patent Attorney who is thoroughly aware of how to address the objections raised in the Examination Report within a time period as given by the Patent Office.
Strategization on Preparing Responses to Examination Reports and Office Actions
Upon receiving the Examination Report and analyzing the objections raised in it, the next step is to draft a response for the same. Drafting of the response to the objections raised in the Examination Report is a skill. Addressing the objections raised in the Examination Report is similar to preparing written arguments for a case.
Amendment to Specification, claims and abstract
In the Examination Report, there are prior arts (previously published/granted documents) which are cited by the Controller to the Applicant. Thus, in view of the prior arts, there is a possibility that amendment of specification, claims and abstract might be required.
Based on how close the prior arts to the invention and if there are any specific objections with respect to drafting of the specification (including claims, abstract and drawings), the Applicant can amend the same in order to overcome the objections and distinguish the invention with the prior arts clearly.
Thus, in order to distinguish the invention from the prior arts through claim amendments so as to overcome the objections raised in the Examination Report, required a highly qualified Patent Attorney.
Attending to Hearings
On filing the response to the Examination Report, the Patent Office (The Controller) shall review the same and if there are still further objections, the Patent Office shall be providing another chance through hearing.
As mentioned above, a hearing can be attended either through video conference or through in person. A hearing can be attended only by the Patent Attorney of the Applicant.
A hearing is a presentation of response to the objections raised in the hearing notice orally. It is a way of orally presenting arguments/explanations to the Controller with respect to the objections raised in the hearing notice.
Preparing and Filing Hearing Written Submissions
After attending the hearing, the arguments/explanations provided during the hearing, needs to be submitted at the Patent Office in the writing as well and therefore, it is termed as ‘written submissions’.
As the Patent Attorney attends the hearing on behalf of the Applicant, it is him who will be able to prepare the written submissions based on the directions/suggestions given by the Controller during the hearing.
Non-filing of the written submissions within a timeline, will result in abandonment of the application which cannot be revived.
Thus, maintaining the deadlines and meeting the same is one of the most important managing skills required for a Patent Attorney.
After filing of the written submissions, if the Controller/Patent Office is convinced, a patent certificate shall be granted in the name of the Applicant. However, if the Patent Office is not convinced, a further opportunity of hearing may be provided by the Patent Office or the application may be rejected/refused.
Pre-Grant Oppositions
The term ‘opposition’ means to oppose or to be against and the term ‘pre-grant’ means before the grant of the patent certificate. Thus, pre-grant opposition means opposing grant of a patent certificate for an application/invention.
A pre-grant opposition can be filed by any interested person which has been defined in the Patents Act under section 2.
A pre-grant opposition requires drafting and filing of an application opposing as to why a patent certificate should not be given to the Applicant. Thus, a pre-grant opposition can be filed by any interested person, at any time, before the grant of the patent certificate.
If the Controller/Patent Office is convinced with the said application, the Controller shall ask the Applicant to reply to the same and would further provide an opportunity of hearing both the parties.
Post-Grants
After a grant of the Patent certificate, there are few requirements that need to be fulfilled by the Applicant which are as follows
Patent Maintenance
After grant of a patent certificate, maintaining the same requires to meet few formal procedures such as filing a statement regarding the working of the invention every year along with a specific fees.
The fees of maintaining a patent is provided in schedule I of the Patents Act, 1970.
Patent Restoration
If the Applicant fails to pay the fee for the maintaining the patent certificate, the patent certificate shall be ceased by the Patent Office after a certain period of time.
Filing Assignments / Licenses
Statement of Working for Patents
Post-Grant Opposition Proceedings